how to find current ratio
What is the Current Ratio?
The current ratio, also known as the working capital Net Working Capital Net Working Capital (NWC) is the difference between a company's current assets (net of cash) and current liabilities (net of debt) on its balance sheet. ratio, measures the capability of a business to meet its short-term obligations that are due within a year. The ratio considers the weight of total current assets Current Assets Current assets are all assets that a company expects to convert to cash within one year. They are commonly used to measure the liquidity of a versus total current liabilities Current Liabilities Current liabilities are financial obligations of a business entity that are due and payable within a year. A company shows these on the . It indicates the financial health of a company and how it can maximize the liquidity of its current assets to settle debt and payables. The current ratio formula (below) can be used to easily measure a company's liquidity.
Image: CFI's Financial Analysis Fundamentals Course
Current Ratio Formula
The Current Ratio formula is:
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
Example of the Current Ratio Formula
If a business holds:
- Cash = $15 million
- Marketable securities = $20 million
- Inventory = $25 million
- Short-term debt = $15 million
- Accounts payables = $15 million
Current assets = 15 + 20 + 25 = 60 million
Current liabilities = 15 + 15 = 30 million
Current ratio = 60 million / 30 million = 2.0x
The business currently has a current ratio of 2, meaning it can easily settle each dollar on loan or accounts payable twice. A rate of more than 1 suggests financial well-being for the company. There is no upper-end on what is "too much," as it can be very dependent on the industry, however, a very high current ratio may indicate that a company is leaving excess cash unused rather than investing in growing its business.
Download the Free Current Ratio Formula Template
Enter your name and email in the form below and download the free template now! You can browse All Free Excel Templates Excel & Financial Model Templates Download free financial model templates - CFI's spreadsheet library includes a 3 statement financial model template, DCF model, debt schedule, depreciation schedule, capital expenditures, interest, budgets, expenses, forecasting, charts, graphs, timetables, valuation, comparable company analysis, more Excel templates to find more ways to help your financial analysis.
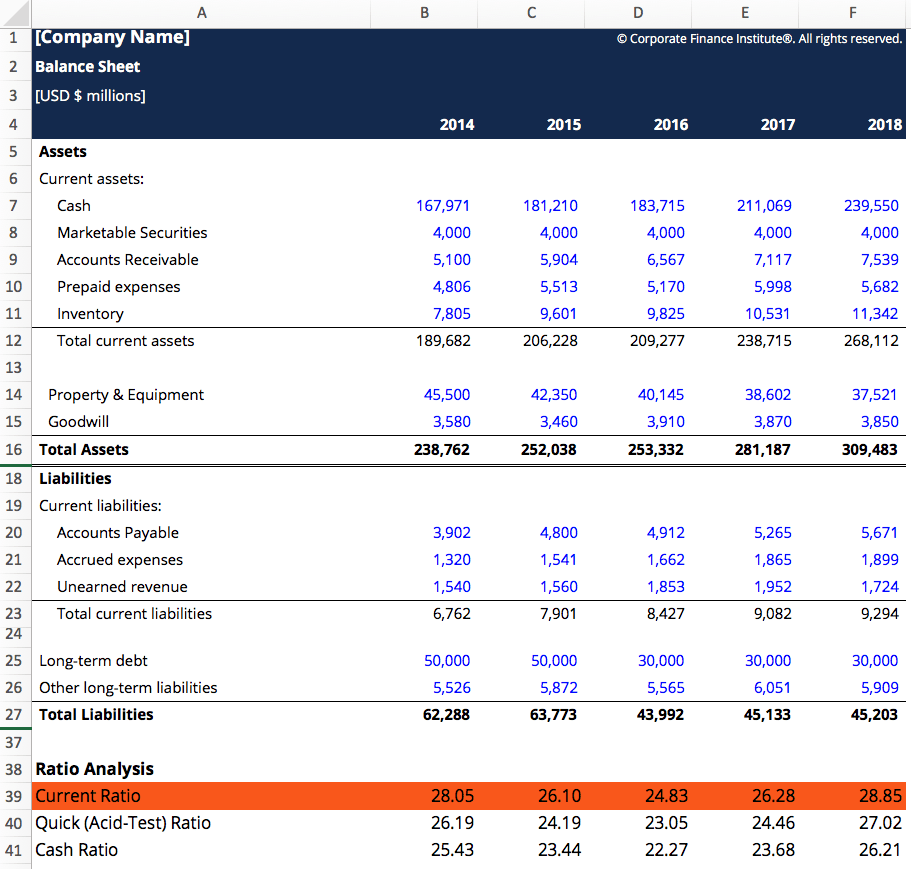
Current Ratio Template
Download the free Excel template now to advance your finance knowledge!
Current Ratio Formula – What are Current Assets?
Current assets are resources that can quickly be converted into cash within a year's time or less. They include the following:
- Cash – Legal tender bills, coins, undeposited checks from customers, checking and savings accounts, petty cash
- Cash equivalents Cash Equivalents Cash and cash equivalents are the most liquid of all assets on the balance sheet. Cash equivalents include money market securities, banker's acceptances – Corporate or government securities with 90 days or less maturity
- Marketable securities Marketable Securities Marketable securities are unrestricted short-term financial instruments that are issued either for equity securities or for debt securities of a publicly listed company. The issuing company creates these instruments for the express purpose of raising funds to further finance business activities and expansion. – Common stock, preferred stock, government and corporate bonds with a maturity date of 1 year or less
- Accounts receivable Accounts Receivable Accounts Receivable (AR) represents the credit sales of a business, which have not yet been collected from its customers. Companies allow – Money owed to the company by customers and that is due within a year – This net value should be after deducting an allowance for doubtful accounts (bad credit)
- Notes receivable Notes Receivable Notes receivable are written promissory notes that give the holder, or bearer, the right to receive the amount outlined in an agreement. – Debt that is maturing within a year
- Other receivables – Insurance claims, employee cash advances, income tax refunds
- Inventory Inventory Inventory is a current asset account found on the balance sheet, consisting of all raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods that a – Raw materials, work-in-process, finished goods, manufacturing/packaging supplies
- Office supplies – Office resources such as paper, pens, and equipment expected to be consumed within a year
- Prepaid expenses Prepaid Expenses Prepaid expenses represent expenditures that have not yet been recorded by a company as an expense, but have been paid in advance. In other – Unexpired insurance premiums, advance payments on future purchases
Current Ratio Formula – What are Current Liabilities?
Current liabilities are business obligations owed to suppliers and creditors, and other payments that are due within a year's time. This includes:
- Notes payable Notes Payable Notes payable are written agreements (promissory notes) in which one party agrees to pay the other party a certain amount of cash. – Interest and the principal portion of loans that will become due within one year
- Accounts payable Accounts Payable Accounts payable is a liability incurred when an organization receives goods or services from its suppliers on credit. Accounts payables are or Trade payable – Credit resulting from the purchase of merchandise, raw materials, supplies, or usage of services and utilities
- Accrued expenses Accrued Expenses Accrued expenses are expenses that are recognized even though cash has not been paid. They are usually paired up against revenue via the matching principle – Payroll taxes payable, income taxes payable, interest payable, and anything else that has been accrued Accrual Accounting In financial accounting, accruals refer to the recording of revenues that a company has earned but has yet to receive payment for, and the for but an invoice is not received
- Deferred revenue Deferred Revenue Deferred revenue is generated when a company receives payment for goods and/or services that it has not yet earned. In accrual accounting, – Revenue that the company has been paid for that will be earned in the future when the company satisfies revenue recognition Revenue Recognition Revenue recognition is an accounting principle that outlines the specific conditions under which revenue is recognized. In theory, there is a requirements
Why Use the Current Ratio Formula?
This current ratio is classed with several other financial metrics known as liquidity ratios. These ratios all assess the operations of a company in terms of how financially solid the company is in relation to its outstanding debt. Knowing the current ratio is vital in decision-making for investors, creditors, and suppliers of a company. The current ratio is an important tool in assessing the viability of their business interest.
Other important liquidity ratios include:
- Acid-Test Ratio Acid-Test Ratio The Acid-Test Ratio, also known as quick ratio, is a liquidity ratio that measures how sufficient a company's short-term assets can cover current liabilities
- Quick Ratio Quick Ratio The Quick Ratio, also known as the Acid-test, measures the ability of a business to pay its short-term liabilities with assets readily convertible into cash
Below is a video explanation of how to calculate the current ratio and why it matters when performing an analysis of financial statements Analysis of Financial Statements How to perform Analysis of Financial Statements. This guide will teach you to perform financial statement analysis of the income statement, .
Video: CFI's Financial Analysis Courses
Additional Resources
Thank you for reading this guide to understanding the current ratio formula. CFI is the official global provider of the Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FVMA)® Become a Certified Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® CFI's Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® certification will help you gain the confidence you need in your finance career. Enroll today! designation. To keep educating yourself and advancing your finance career, these CFI resources will be helpful:
- Quick Ratio Template Quick Ratio Template This quick ratio template helps you calculate the quick ratio given the amount of cash, marketable securities, accounts receivable and accounts payable. The Quick Ratio, also known as the Acid-test or liquidity ratio, measures the ability of a business to pay its short-term liabilities by having assets that are readily
- Net Asset Liquidation Net Asset Liquidation Net asset liquidation or net asset dissolution is the process by which a business sells off its assets and ceases operations thereafter. Net assets are the excess value of a firm's assets over its liabilities. However, the revenue generated by the sale of the net assets in the market might be different from their recorded book value.
- Liquidation Value Template Liquidation Value Template This liquidation value template helps you compute the liquidation value given a company's total liabilities and assets in auction value. Liquidation value is an estimation of the final value which will be received by the holder of financial instruments when an asset is sold, typically under a rapid sale process. A busi
- What is financial modeling? What is Financial Modeling Financial modeling is performed in Excel to forecast a company's financial performance. Overview of what is financial modeling, how & why to build a model.
how to find current ratio
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/finance/current-ratio-formula/
Posted by: riveraselamudder.blogspot.com

0 Response to "how to find current ratio"
Post a Comment